Introduction to PKI Systems
A PKI system consists of several components. These components have several relationships and dependencies on each other and together form a PKI system:
Certification Authorities
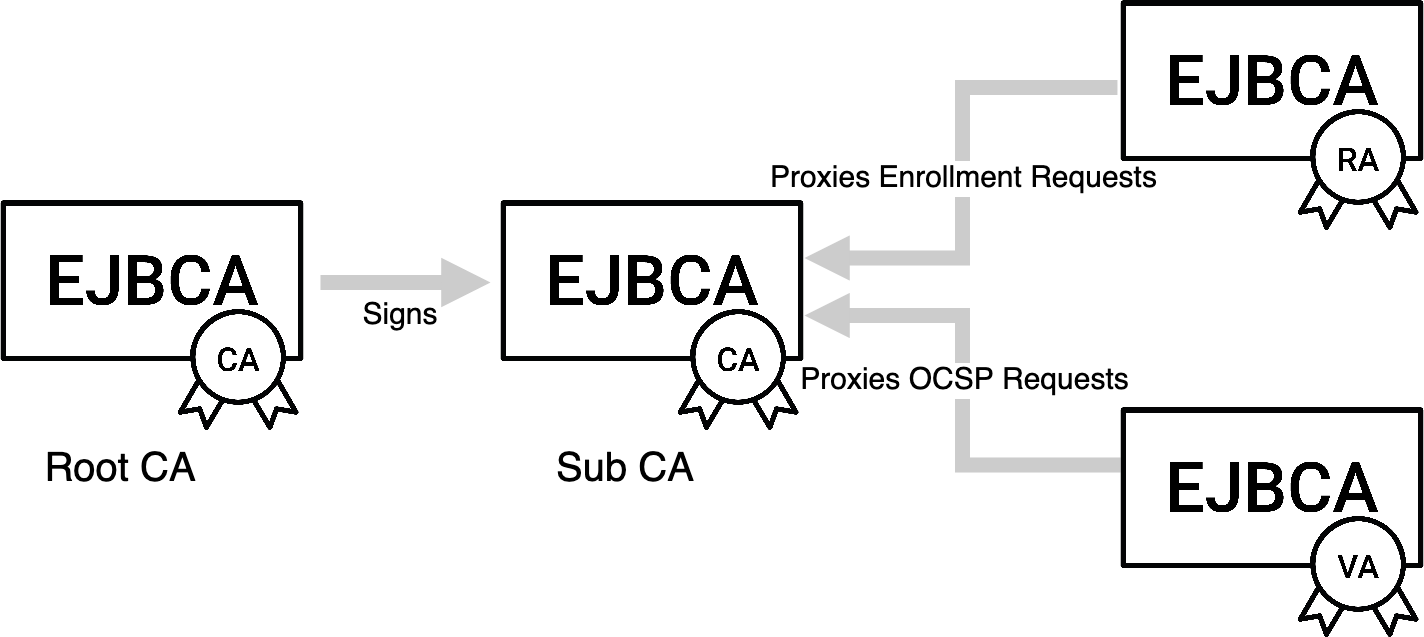
A Certification Authority (CA) issues and verifies certificates. The CA is responsible for maintaining the security of the service through the provisioning of technical and procedural controls in order to ensure that certificates are only issued to appropriate entities. As illustrated in the figure, the CA collects certificate requests from the registration authority and returns a certificate back to the subscriber.
Registration Authority
The part of the infrastructure that collects and verifies requests for certificates is called the Registration Authority (RA). The RA implements the procedural and vetting requirements for ensuring that the certificates are only issued to claimants. The RA implements procedures for establishing the identity of the applicant.
Validation Authority
The Validation Authority (VA) provides revocation services. As a piece of digital data, a certificate cannot be retrieved from the entity to which it is issued. Revocation involves placing the certificate on a blacklist so that the issued certificate can no longer be used for the purpose for which it was issued. The blacklist is commonly referred to as a Certificate Revocation List (CRL). Another commonly used procedure for revocation checking is to publish a protocol where by external entities may query whether a certificate is revoked. This protocol is called the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP). A server that facilitates OCSP checking is Ver:2.2 commonly referred to as an OCSP server. Within the context of a PKI system described in this section, CRL publishing and online OCSP services are provided by the Validation authority. Thus as illustrated below, the relying party may query the validation service on the authenticity of a certificate and reply back on the result as illustrated in the figure.
Dissemination Services
Certificates, once issued, need to be disseminated to the outside. This can be achieved by publishing them to external repositories: LDAP, Active Directory and others.
PKI Aware Applications
PKI Aware Applications: Applications that rely on security mechanisms provided by PKI are often referred to as PKI aware applications. These applications are able to interpret, verify and use certificates to provide additional services. Examples of PKI aware applications include digital signing applications and encryption applications.
Relying Parties
A relying party is the party that relies on the information provided by the trust service provider. As there is no direct relation between the trust service provider and the relying party, the party has to base its trust on various aspects of the trust service provider. These would include reputation, presence of any relying party agreements, policies and practice statements and so on.
Subscribers
The subscriber is the legal entity to which a certificate is issued by the certification authority. Relations between the subscribers and certification authorities are governed by subscriber agreements. A subscriber may be a person, a device or any other tangible device capable of owning a certificate and being identified by it. Other terms used to describe a subscriber are end entity, user (for certificates issued to persons) and subject.
Trust Center
At the heart of the PKI system is the requirement to provide a centralized trusted service where relations between previously unknown entities may be established through a trusted party. Thus as there is no natural relationship of trust between the subscriber and the relying party although the subscriber trusts the CA and the relying party also trusts the CA an indirect trust relationship is established between the subscriber and the relying party. The question arises as to why the relying party should trust the CA. This is because of its' containment within a trust center. A trust center implements processes, procedures and other security technology that make it extremely difficult to request a certificate without validating the identity of the subscriber.
%20(500%20x%20162%20px)(1).png)